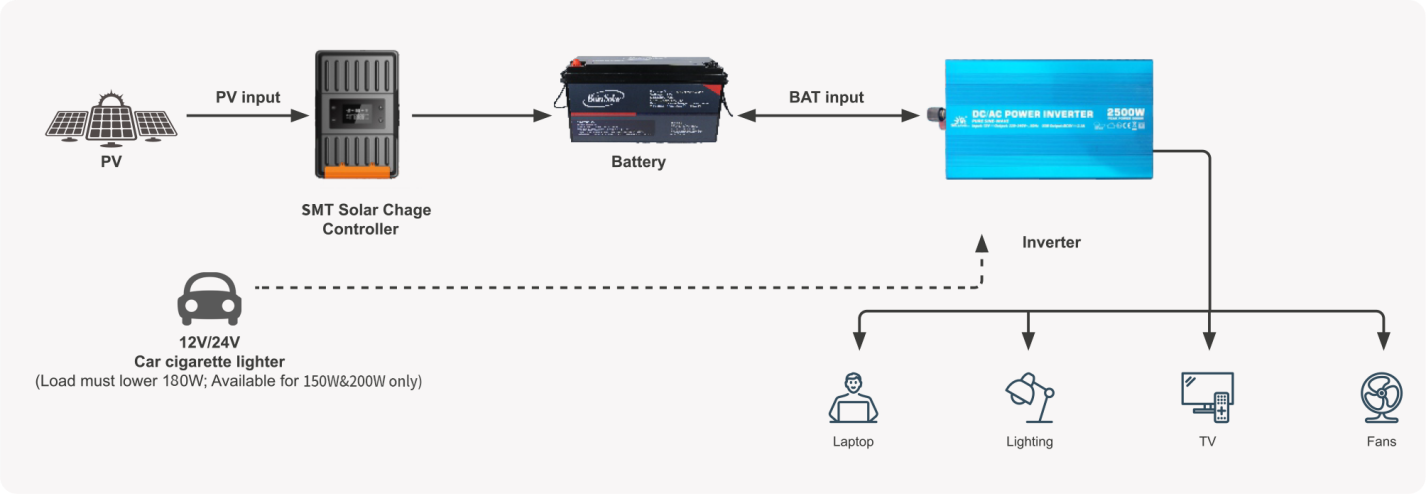
1. Car Inverter: Definition and Function
A car inverter is a device that transforms the direct current (DC) from a car battery into alternating current (AC), which is commonly used in homes and industries. This conversion enables the use of various standard AC appliances in the vehicle, such as laptops, mobile phone chargers, car refrigerators, and even small household items, enhancing the travel experience.
2. Technical Principles and Classification
The car inverter operates based on power electronics technology, using internal power semiconductor devices like MOSFETs or IGBTs for high-frequency switching to efficiently convert DC into AC. Car inverters are typically classified by output power into three categories:
- Low power (100W-300W)
- Medium power (300W-1000W)
- High power (above 1000W)
These variations cater to the diverse needs of users. Additionally, car inverters are available in two types:
- Pure sine wave inverters: The output waveform resembles the home power grid, making it suitable for devices requiring high-quality power.
- Modified sine wave inverters Provide a more basic waveform suitable for less sensitive devices.
3. Application Scenarios and Value
- Outdoor Adventure and Camping: Car inverters enhance outdoor experiences by making activities like cooking, charging devices, staying connected, and enjoying music more convenient.
- Long-Distance Travel: On extended drives, car inverters provide continuous power, enabling children to watch cartoons, adults to manage work emails, or passengers to enjoy the entertainment system without interruptions.
- Emergency Rescue: In the event of natural disasters or emergencies, a car inverter serves as a temporary power source, supporting essential devices like mobile phones, flashlights, and radios, ensuring communication and aiding in self and mutual rescue efforts.
4. Selection and Maintenance Recommendations
Choose the Appropriate Power: Based on your needs, select an inverter with the right power capacity to avoid energy waste or insufficient power supply.
Ensure Proper Heat Dissipation: Since inverters generate heat during operation, install them in well-ventilated areas to prevent overheating from prolonged use.
Regular Inspection: Periodically check the inverter’s connections, wires, and plugs to ensure they are secure and undamaged. Also, monitor the vehicle battery’s voltage to avoid starting the inverter under low power conditions.
Brand and Quality: Choose a reputable brand to ensure high product quality and access to professional after-sales service.
Post time: Feb-24-2025